
Pathological jaundice can present on day 1 or it can be prolonged, persistent after day 14 in the term infant or day 21 in the preterm infant. Pathological jaundice, on the other hand, should raise concern and always requires further investigation. Serum bilirubin (SBR) levels will peak by day 4 and reduces by day 14. Jaundice is classified as physiological or pathological. Physiological versus pathological jaundice Alterations at any of these stages can result in jaundice ( Table 64.1). There are four stages involved in bilirubin metabolism. In order to provide informed care for a jaundiced baby and parents it is important to have an understanding of bilirubin metabolism. Jaundice in the newborn is common, occurring in over two-thirds of term infants and even more frequently in the preterm infant. doi: 10.1002/lt.24640.Jaundice occurs when bilirubin accumulates in the extravascular fatty tissues (skin and brain). Biliary atresia: Indications and timing of liver transplantation and optimization of pretransplant care. Sundaram SS, Mack CL, Feldman AG, Sokol RJ.Biliary atresia: Potential for a new decade. Prolonged neonatal jaundice: When to worry and what to do. Neonatal jaundice: Aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Paediatric referral is indicated for early-onset jaundice (within 24 hours of life), prolonged jaundice and conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia.Regular clinical reviews, including growth assessments, are recommended until bilirubin levels are reassuring are within normal ranges.A thorough history and physical examination are vital in assessing a neonate with hyperbilirubinaemia.On follow-up review, her jaundice had resolved, and her weight gain improved.
#Bilirubin levels in pathological jaundice full
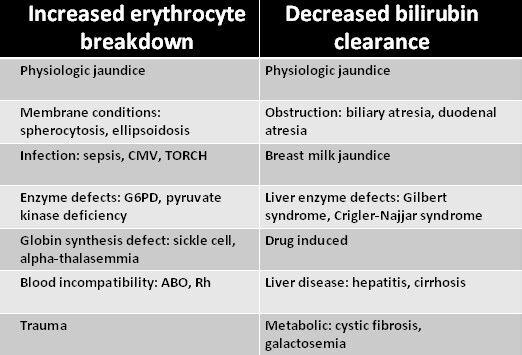
Initially she required partial parenteral nutrition because of malnutrition, but she transitioned to full enteral feeds once reaching an adequate weight and was discharged with frequent gastroenterology and GP reviews. The patient underwent the Kasai procedure. Children who remain jaundiced after the Kasai procedure are at risk of fat malabsorption and malnutrition and typically require vitamin supplementation. 5,7 Monitoring for progressive portal hypertension, worsening malnourishment and ascending cholangitis is required. The Kasai procedure is considered a palliative procedure, and children with this condition remain at risk of progressive liver fibrosis even after successful procedures. The patient’s liver enzymes were abnormal, with gamma-glutamyl transferase 285 U/L (reference range 15–132 U/L), alanine aminotransferase 539 IU/L (reference range 100 days because of poor likelihood of jaundice clearance older children would be considered for early liver transplantation. Always pathological if 35 μmol/L or if the conjugated bilirubin fraction is >20% of the total bilirubin.Pertinent questions on the history of a neonate with hyperbilirubinaemia 1 Important questions on history are outlined in Table 2. Answer 2Ī thorough history can help identify risk factors and the cause of hyperbilirubinaemia. Neonates with hyperbilirubinaemia should be reviewed at least every 48 hours to ensure improvement in the bilirubin levels and adequate weight gain. Breastmilk and physiological jaundice are diagnoses of exclusion, only to be diagnosed after initial investigations are normal (blood group, direct antiglobulin test, thyroid function test and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase screen). Conjugated jaundice: biliary atresia, neonatal hepatitisĬauses that must be urgently ruled out include infections and biliary obstruction.Inherited deficiencies of glucuronyl transferase enzymes (very rare).Physiological jaundice that may be exacerbated by/associated with:.Intermediate (2–14 days of life): Common and mostly benign The differential diagnosis for neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia 1,2Įarly (within 24 hours of life): Pathological


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
